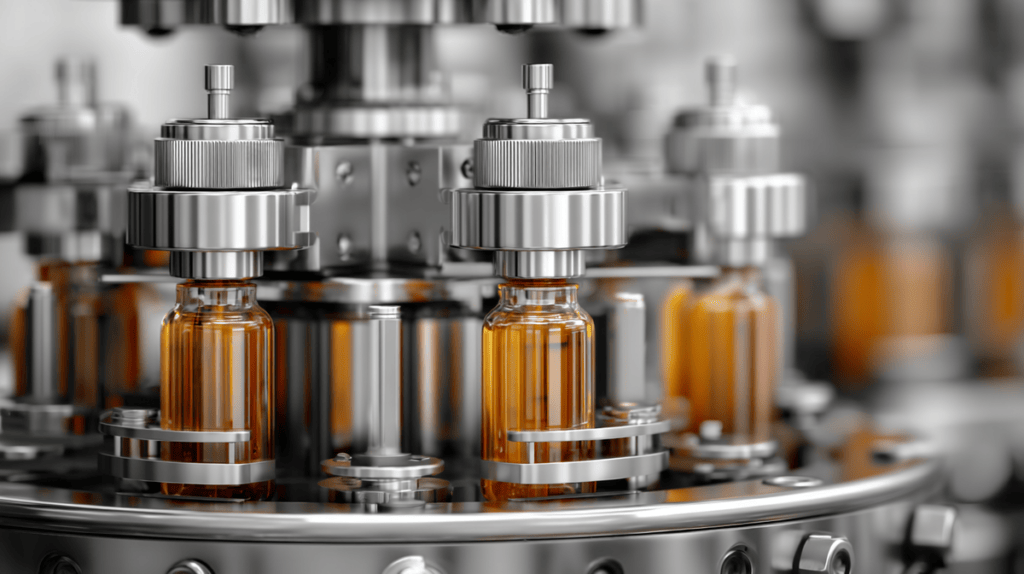
In the world of manufacturing and production, efficiency and precision are paramount. One of the key components that contribute to these factors is the filling machine. These machines are integral to various industries, ensuring that products are filled accurately and consistently. From food and beverages to pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, filling machines play a crucial role in the production process. This article delves into the workings of industrial filling machines, exploring their applications and significance in modern production lines.
How Industrial Filling Machines Work
Industrial filling machines are designed to fill containers with a precise amount of product, whether it be liquid, powder, or granules. The operation of these machines can vary significantly depending on the type of product being filled and the specific requirements of the production line. Generally, filling machines operate through a series of automated processes that ensure accuracy and efficiency.
At the core of a filling machine is its ability to measure and dispense the correct amount of product. This is typically achieved through volumetric or gravimetric methods. Volumetric filling involves measuring the volume of the product, while gravimetric filling measures the weight. Both methods have their advantages, with volumetric filling being faster and gravimetric filling offering higher accuracy.
Filling machines are equipped with sensors and control systems that monitor the filling process. These systems ensure that each container is filled to the correct level, minimizing waste and ensuring consistency. Additionally, many modern filling machines are designed to handle a variety of container sizes and shapes, making them versatile tools in any production line.
Applications of Filling Machines in Production
Filling machines are used across a wide range of industries, each with its unique requirements and challenges. In the food and beverage industry, filling machines are essential for bottling liquids such as juices, sauces, and oils. These machines must adhere to strict hygiene standards to ensure product safety and quality.
In the pharmaceutical industry, filling machines are used to fill vials, ampoules, and syringes with medications. Precision is critical in this sector, as even the slightest deviation in dosage can have significant consequences. Therefore, pharmaceutical filling machines are designed with advanced features to ensure the highest level of accuracy.
The cosmetics industry also relies heavily on filling machines to package products such as creams, lotions, and perfumes. These machines must be capable of handling a variety of viscosities and container types, from tubes to bottles.
One specific application of filling machines is in a bottling line. Bottling lines are complex systems that integrate filling machines with other equipment such as cappers, labelers, and conveyors. These lines are designed to streamline the bottling process, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
The Future of Filling Machines
As technology continues to advance, the future of filling machines looks promising. Automation and digitalization are set to play a significant role in the evolution of these machines. With the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence), filling machines are becoming smarter and more efficient.
Predictive maintenance is one area where technology is making a significant impact. By using sensors and data analytics, manufacturers can predict when a machine is likely to fail and perform maintenance before it becomes a problem. This not only reduces downtime but also extends the lifespan of the equipment.
Furthermore, the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly packaging solutions is driving innovation in the design of filling machines. Manufacturers are developing machines that can handle biodegradable and recyclable materials, reducing the environmental impact of packaging.
In conclusion, filling machines are indispensable in modern production lines, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility. As industries continue to evolve, these machines will undoubtedly adapt to meet new challenges and opportunities, ensuring their continued relevance in the manufacturing landscape.

 Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) & Unique Author
Annamae Solanoric is the Chief Marketing Officer and a distinctive voice within the company as a unique author. Combining her passion for storytelling with her deep expertise in branding and digital marketing, she not only leads the company’s marketing strategies but also crafts compelling narratives that engage and inspire audiences. Her work as an author has been widely recognized, and she seamlessly integrates her creative vision into building the company’s brand. Annamae’s leadership in both marketing and content creation drives innovation and helps establish strong connections with clients and partners alike.
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) & Unique Author
Annamae Solanoric is the Chief Marketing Officer and a distinctive voice within the company as a unique author. Combining her passion for storytelling with her deep expertise in branding and digital marketing, she not only leads the company’s marketing strategies but also crafts compelling narratives that engage and inspire audiences. Her work as an author has been widely recognized, and she seamlessly integrates her creative vision into building the company’s brand. Annamae’s leadership in both marketing and content creation drives innovation and helps establish strong connections with clients and partners alike.